Articles and Recipes
Brain Nutrition
Diets associated with improved cognition and mental health.
A healthy and active lifestyle, with sufficient exercise and sleep, as well as avoiding harmful substances such as alcohol, nicotine, or excessive sugar, can protect the brain.
Current studies show that stroke and dementia are among the top 10 causes of death.
On World Brain Day, the German Society of Neurology pointed out that too much sugar can harm the brain.
Drinking more than three cups of coffee a day is linked to faster cognitive decline, suggest the results of a large study.
Studies have evaluated a diet with intermittent fasting and a standard healthy diet, focused on healthy foods; both led to weight loss, reduced insulin resistance, and delayed brain aging in overweight older adults.
In young people, studies show that healthy diets correlate with mental health: healthier foods reduce internalizing and externalizing disorders, while typical Western diets increase the risk. Dietary interventions include higher levels of fruits and vegetables, fish and nuts, and lower levels of processed foods.

Forget about injections!
Foods that release appetite-suppressing hormones
Injectable weight-loss drugs, such as Mounjaro, Ozempic and Saxenda, have been getting all the praise lately, but they're not for everyone.
If the yo-yo effect, or the side effects, muscle loss, or the cost of weight loss medications don't convince you, another approach can increase satiety through the same pathway (GLP-1).
So how do you do this and how does it work? In theory, all you need to do is boost your gut microbiome.
To increase the variety of microbes in the gut, especially in the lower intestine and colon—producers of appetite-suppressing hormones—it's crucial to know that they feast on the fiber from the food you eat and transform it into substances your body needs; these substances send signals throughout your body.
If you don't have enough microbes or you have too many "wrong kinds," this influences these signals, which can lead to increased hunger and various health problems.
Weight gain in middle age is not inevitable for women.
Middle age (40-65 years) is characterized by physical, psychological, and social changes, rooted in a combination of the natural aging process and the menopausal transition.
During this phase of life, 60%-70% of women report weight gain with predominantly central (abdominal) fat deposition.
Although we generally reduce our caloric intake as we age, we also decrease our energy expenditure as a result of reduced physical activity and a notable loss of muscle mass: from the age of 30, muscle mass decreases by 3% to 8% per decade.
Excess adiposity is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death among women, and breast cancer, the most common cancer in women.
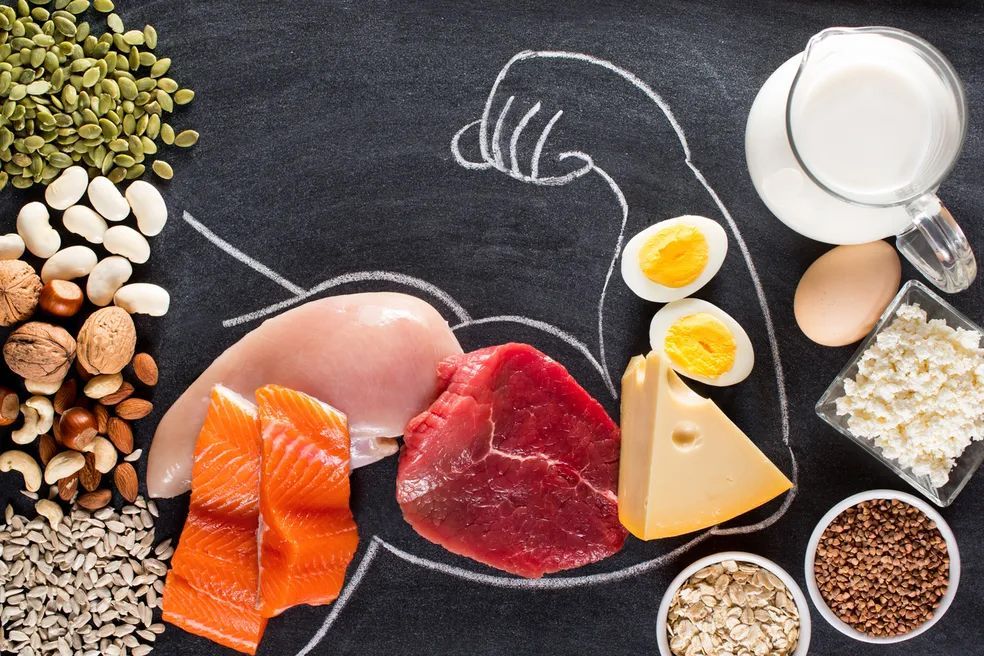

So, how much protein should I eat?
From the low-fat craze of the late 1980s (“fat makes you fat”) to the shift away from carbohydrates in general and sugar in particular in the 1990s and 2000s, we have now arrived at what appears to be a fascination with protein.
High-protein diets, such as the Paleo and Zone diets, are gaining popularity. And while the increasingly popular ketogenic diet is more anti-carbohydrate than other high-protein diets, any diet that limits one macronutrient will increase the concentrations of the others.
It makes some sense that high-protein diets would be good for you. The good things inside your body (like muscles) are made of protein, and you are what you eat, right? But the data doesn't necessarily support the claim that high protein consumption is actually very healthy.
Intermittent Fasting
Advantages vs. Disadvantages
Fasting has been used in therapeutic, cultural, and religious practices and traditions for thousands of years. When fasting, the body undergoes ketosis and experiences a metabolic shift in its fuel source: from glucose to fatty acids. Fasting may not be ideal for all patients, such as pregnant women, people with type 1 diabetes, or those who have or are at risk of developing an eating disorder.
However, if appropriate for a patient's personalized treatment strategy, the benefits of fasting may include improvements in several areas, such as mental or cognitive performance, cardiovascular health, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and the effectiveness of cancer treatments.


Food and
kidney stones
There is growing evidence that nephrolithiasis is a systemic disease, as opposed to the former belief that it was an isolated urinary metabolic disease, since considerable links have been found between nephrolithiasis and chronic diseases such as hypertension, obesity, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance.
Kidney stones are a multifactorial disease, and a large number of etiological factors can be adequately modified through diet, since it should be considered that urine composition is directly related to food intake.
In fact, changing habitual inadequate eating patterns should be the primary measure to prevent kidney stones. Dietary interventions can reduce the risk of urinary stone formation and recurrence. Each patient with nephrolithiasis should undergo dietary adjustments according to the composition of the stone.
Sweetening
In recent times, there has been a significant increase in the number of published studies addressing the health risks caused by sweeteners; the WHO has also spoken out, classifying them as harmful to health and weight loss.
The concern with consuming foods high in sugar is that they can raise blood sugar levels, increase triglycerides, cause oxidative stress to the body, and lead to weight gain.
The big question that remained was: what would be the healthiest way to sweeten desserts and drinks?
Precision nutrition:
Nutrigenomics and personalized diets
A person's gene-nutrient interactions, as well as variations in the composition of the gut microbiome, are fundamental components in dietary planning.
Metabolomics identifies the molecules and metabolites found in the body and can be used to determine potential biomarkers of disease risk and track the effects of specific foods.
Nutrigenomics, on the other hand, explores how individual genetic differences play a role in how an individual responds to diet, the variability in glucose responses, and the overall impact of diet.
There are a variety of tests available: Nutritional Genomics, Urine Metabolomics, Gut Microbiota Mapping, etc.
The health benefits of postbiotics
When prebiotics are fermented by the gut microbiota, metabolites and byproducts are generated that are beneficial to health.
These postbiotics demonstrate potential immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer properties and possibly help to inhibit pathogens.
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs): butyrate, propionate, and acetate are examples of postbiotics.
Artificial sweeteners:
the sugar-free paradox
According to new guidelines from the WHO (World Health Organization), artificial sweeteners should not be used in weight-loss diets.
The document warns of a lack of scientific consensus regarding its effectiveness in weight management and of long-term side effects, such as an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer. Read more>>
The best diets for heart health
An evidence-based analysis rated, on a scale of 1 to 100, how well 10 popular diets align with the AHA's (American Heart Association) dietary advice for heart-healthy eating.
The 10 diets evaluated were: DASH, Mediterranean, Pescatarian, ovo-lacto vegetarian, vegan, low-fat, very low-fat, low-carbohydrate (paleolithic), and very low-carbohydrate (ketogenic). Read more>>
Gut Health
"All diseases begin in the gut" - Hippocrates
Our digestive tract is home to the gut flora, a highly complex group of bacteria and other microorganisms that influence immunity, inflammation, metabolism, and more.
An unbalanced gut microbiota has been associated with several health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, depression, and autoimmune diseases.















